Grant Differenzenmaschine
|
1 Maschinendaten
Modell............: ohne
Firma.............:
Hersteller*.......: Grant, George B.]
Ort, Land.........: USA
Maße (LxBxH)......: 2500 x x 1500 cm (Grundkörper)
Maße (LxBxH)......: x x cm (mit Bedienelementen)
Gewicht...........: 900 kg
Stellen (EWxUWxRW): x x
Eingabe mit.......:
Antrieb...........:
Löschung..........:
System............: Differenzenmaschine
Farbe(n)..........:
Material..........:
Produziert........: s. unten
2 Beschreibung
Beschreibung......: Die Maschine war ausgestellt bei der Weltausstellung Philadelphia 1876. Sie erreichte im Gegensatz zu ihren Vorgängern anderer Erfinder keine grosse Bekanntheit.
Besonderheiten....:
The Difference Engine. This is a large machine built for the University
of Pennsylvania, and designed for the construction of large mathematical
tables, such as tables of logarithms, sines, tangents, reciprocals, square
and cube roots, etc. It computes the terms of any such table, and prepares
a mould of them stamped in wax, from which an electrotyped plate is made,
ready for the press. It stands five feet in height by eight in length,
weighs 2000 lbs., contains, when in full working order, some 15,000 pieces,
and is worth about $10,000.
The Calculating Machine is a smaller instrument for common operations in
multiplication, division, etc. It is a foot in length by half as much in
height and width, weighs twenty pounds, and contains less than 400 pieces,
less than 75 of which are working parts. It takes numbers up to nine decimal
places. Its mechanism is simple, strong, and durable; its manipulation is easy."
Designer..........:
Zeitgenössische Beschreibungen:
Varianten.........:
Konstrukteur*.....: George Barnard Grant (1849-1917), s. a. 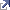 http://history-computer.com/Babbage/NextDifferentialEngines/Grant.html
http://history-computer.com/Babbage/NextDifferentialEngines/Grant.html
Eine Übersicht zu seinen Maschinen gibt
Annual Record of Science and Industry for 1876. New York 1877, S. 43 / 44:
"CALCULATING MACHINES.
Mr. George B. Grant, while a student of the Lawrence Scientific School,
invented a new and simple form of calculating machine, which is now on
exhibition in Machinery Hall, Philadelphia. Two styles are now made,
the first being for special use, while the second is intended for use
in counting houses, insurance offices, etc.
3 Weitere Bilder
4 Literatur
- s. auch Grant Rechenmaschine
5 Patente
6 Weblinks
7 Seriennummern
- Seriennummern:
- Nummernlagen:
8 Allgemeine Anmerkungen
Seite eröffnet von: stewe 10:16, 19. Mai 2010 (CEST)
Diese Seite darf an allen Stellen ergänzt werden,
die noch leer sind. Außerdem dürfen Zeilen hinzu gefügt werden.
Falls Sie mit einem bestehenden Inhalt nicht einverstanden sind,
machen Sie bitte einen Eintrag bei der Diskussion und schicken dem Ersteller der Seite eine Mail.
![[Hauptseite]](/upload/wiki.png)
 Hauptseite
Hauptseite

 siehe unten
siehe unten